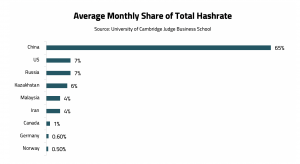
It’s in the beginning of March when news about US and China’s contention started to pop-up as The Biden Administration is putting efforts to limit China’s access to technology by revealing a plan to rally an alliance of nations to fight for an edge in various technological areas. However, after the sanctions imposed by the U.S. against Huawei last year, these recent U.S. plans are not much of a surprise to China which has already started taking a leap into technological self-sufficiency. One of the areas of technology in which China desires to have the upper hand, is the blockchain technology which is the base for cryptocurrency transactions. It is also working on curbing the hegemony of the U.S. over cryptocurrencies by declaring war on individually owned crypto mining, eventually increasing the price of cryptocurrencies. In fact, China accounted for 65% of Bitcoin mining capacity as of April 2020, in comparison to 7.2% in the U.S. By which, China announced Inner Mongolia has banned cryptocurrency mining and declared it will shut all such projects by April 2021. Now that this policy is applied over all the Chinese provinces, trading cryptocurrencies is banned in China, and Bitcoin mining is becoming illegal!
Context of China’s War on Crypto Mining:
The announcement of the crypto-mining ban policy goes back to 2019 when speculations have incremented over fraud and energy waste that results from the computer processing of cryptocurrencies. According to the draft Policy released back then, Beijing has vowed to halt carbon emissions per unit of GDP by 3% this year and limit incremental growth of energy consumption to about 5 million tons of standard coal which come mostly from coal-fired plants (such as those generating electricity for bitcoin mining equipment), and other heavy industries. Therefore, while China has taken steps to urge provinces to reduce their energy consumption, Inner Mongolia, which accounted for 8.7% of bitcoin mining in China because of its cheap power, is set to ban crypto mining by April 2021, while also banning new digital coin projects to constrain growth in energy consumption to about 1.9% in 2021. In addition to environmental concerns that are not even offset with adequate profit to the government, China is not in favor of unregulated financial markets within its territory by disallowing financial institutions in cryptocurrency transactions. Meanwhile, it desires to possess control over the crypto by allowing state-owned banks to launch their own blockchain projects as well as establishing a state-initiated cryptocurrency.
US-China Tensions – A Series of Confrontational Events:
The Pivotality of the role of Bitcoin in the global Financial System happens to be because Bitcoin, among other cryptocurrencies, is seen as an inflationary and geopolitical risk hedge, meaning that when there are tensions between global powers or when global crises, like COVID-19 Pandemic hit, Bitcoin remains resilient from a price perspective. Most importantly, the institutional investment interest in Bitcoin comes from the availability of Bitcoin access 24/7, irrespective of countries and borders. Noteworthy, is that a war on crypto mining would cause a surge in the prices of cryptocurrencies, which explains in a way the urge to shut down on crypto mines. Until we reached that era of digital assets, the U.S. used to have influence over the exchange of analog money and property around the world, basing any international exchange on dollar, the U.S. had a gatekeeping role over almost all financial transactions. Nonetheless, China wants to write the ending sentences of this era by challenging the U.S. financial hegemony. It is easy to be spotted that the Chinese government is in a retaliation mode after the Trump Administration calling for the U.K. into joining its ban against Chinese mobile provider Huawei’s 5G wireless business along with other sanctions.
While the U.S. seeks to protect the U.S. dollar as global reserve currency, China aspires to export its own economic model around the world. Therefore, China is adopting consistent steps towards:
- Executing a digital currency project, known as Digital Currency Electronic Payments, or DCEP, which is Blockchain-integrated so that the wide range of this technology would allow the Chinese government to spread adoption of its digital currency. This could be a way that enables Chinese entities to avoid U.S. financial oversight.
- In addition, the government granted six public blockchains access to its Blockchain Services Network and the Chinese supreme court called for stronger definitions of private citizens’ digital currency property rights.
- Moreover, as another way of retaliating, Ant Group ($200 billion), which runs Alibaba’s Alipay mobile payments platform, announced its public listing won’t occur in New York this time but in Shanghai and Hong Kong, so that U.S.-based investors would now be denied access to this giant primary share offering and the U.S. wouldn’t have regulations over China’s payment systems.
- As China accounted for 65% of crypto-mining capacity as of April 2020, the aforementioned ban would cause a surge in the prices of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies and the Chinese digital currency project that will bypass the US payment systems which the US has used to enforce sanctions.
East-Asia Cryptocurrency Scheme vs. Libra Plan:
A new phase of the tech contest has started when China created an East Asia cryptocurrency scheme, and the American social media company Facebook announced its Libra plan. Basically, the Chinese plan is to create a digital currency consisting of the Chinese yuan, Japanese yen, South Korean won and Hong Kong dollar. China’s central bank started testing the digital Yuan in several provinces in the country and encouraging the private sector to contribute to this initiative. The planned regional cryptocurrency is a cross-border payment network that is supposed to expand international trade, it might as well support a free trade agreement between the four countries. This proposal is in line with China’s attempt to strengthen its ties with the three other countries in response to the US decoupling of China. At the same time, it aspires to have its currency used internationally. Above all, China intensified its studies about the digital Yuan when the Libra cryptocurrency revised plan was announced by Facebook in June last year. The initial Libra plan was to create a basket of digital currencies, and then it was revised to offer separate coins backed by individual fiat currencies such as the dollar and euro, due to concerns from financial regulators claiming that the use of different currencies in a single country would weaken the effect of monetary policy. As the US monetary authorities are skeptical about the plan, they still remain uncertain.
Are There Other International Players and What are Their Stances?
The region is divided into supporters of the Libra plan, skeptical countries and others who wish to work independently. An example of countries that support the Libra Plan is Singapore. Singapore’s Temasek announced that it joined the Libra currency along with the dollar, the euro and the pound. On the other hand, the Japanese Yen was dropped from the single-currency digital coin of the Libra plan. Japan believes that it is risky to expose a digital Yen internationally while it is actually unattractive and could witness low volume of transactions. Therefore, in Japan the monetary authorities are yet to decide on how they want to position their currency globally.
Worthy of mentioning is the North Korean Case. Similar to China, North Korea is faced with US economic sanctions that it started to develop a creative way out from the financial restrictions, which is cryptocurrency. It can effectively mine or steal bitcoin to support its economy and missile program thanks to an abundance of cheap energy from coal, while its isolation from the world is a blessing in a way that its mines are unreachable and unsupervised, contrary to the Chinese case.
Likewise, the crippling US sanctions imposed on Iran are causing a heavy burden on the economy. However, a way out could be the possession of a large global crypto mining share. Actually, Iran is trying to use crypto mining as a source of income for the country. Therefore, it is trying to obstruct private crypto mining in an attempt to state-control the revenue stream out of it. Therefore, the state had to shut down several crypto mines particularly after a power outage has occurred and obliged others to register with the Ministry of Industry, Mines and Trade and disclose their identities, the size of their farms with high tariffs on their energy consumption from 482 rials to 1,930 for kilowatt per hour (in U.S. dollars, from 0.1 cent to 4.6 cents). Iran also made deals with foreign investors for crypto mining from China, Turkey, United Arab Emirates and Ukraine with new bills generating income for the country away from the hands of the US. With a continuous increase in Iran’s share in the industry, it is expected that Iran will regain its power in the Middle East and might as well influence the oil market by entering the business with cryptocurrencies.
The Future of Cryptocurrency in a De-globalizing Post COVID-19 World:
- De-globalization
Shedding the light on the shift in global economic trends after the coronavirus pandemic could indicate that the world is moving towards a state of de-globalization where self-sufficiency and localization are the new trends. These notions in fact create a paradox between the aspirations of monetary expansion and financial freedoms and the protection of national financial systems.
- A New Financial Order?
The contest between the US and China over the control over the Blockchain technology is seeing two distinguishable approaches. It is that the US aims at maintaining the decentralization of the crypto while encouraging private investors to build their own crypto mining facilities in the US. On the other hand, China is taming down all individually owned crypto mines in an attempt to state-control it. China might succeed in its plan in diminishing the US hegemony as the global reserve status and reduce its strength as a financial power globally. However, it is unlikely that China beats the US on all fronts especially that the war between both countries does not only involve digital currencies and blockchain technologies, but it also includes other aspects like economic systems, arms race, geopolitical dynamics and human rights, of which the tech war occupies a humble space. Nonetheless, the urge of a tech-based escape from US financial systems is becoming a great demand to curb the excessive sanctions imposed by the US on its rivals.